📌 TL;DR: To win in AI search visibility, you must implement Generative Engine Optimization. This means moving beyond keywords and directly answer specific queries and earning third-party citations.
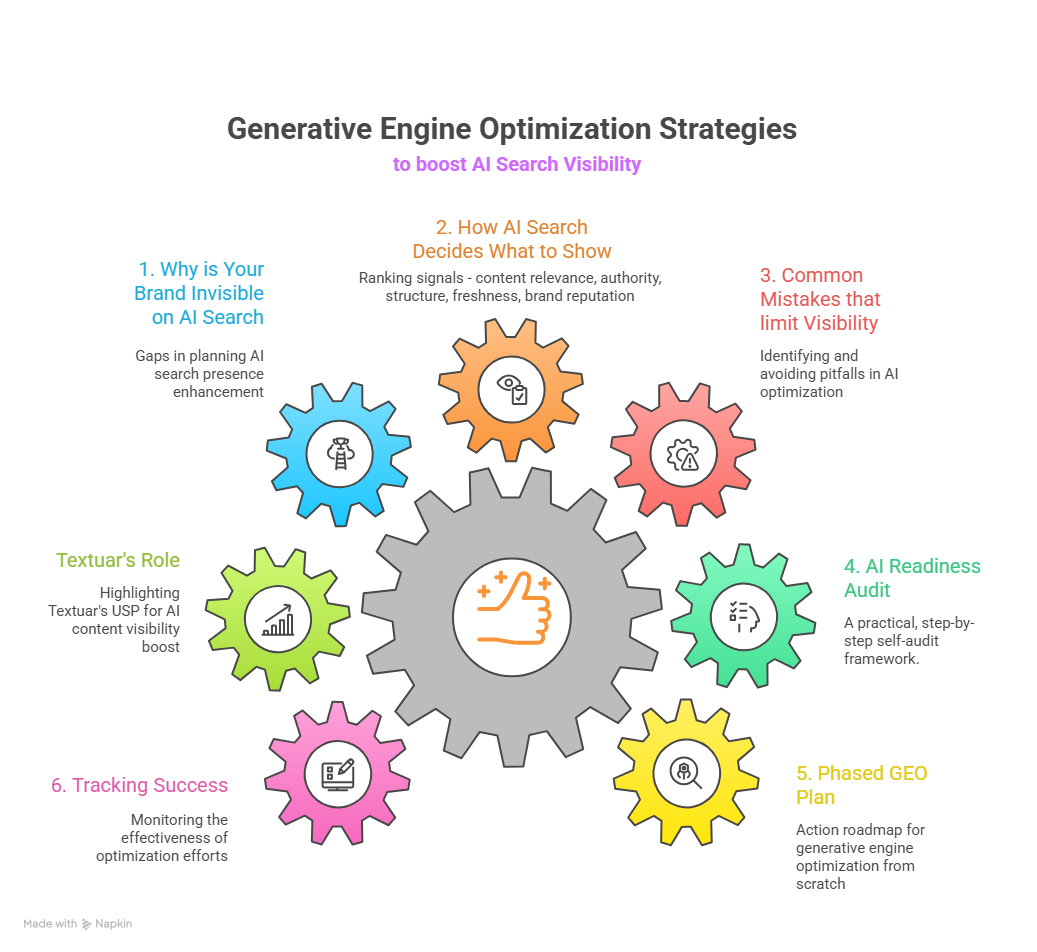
This blog covers-
• Why Your Brand Is Invisible to AI Search (Even If Google Loves You) – We cover the issue as a visibility gap, not an SEO gap.
• How AI Search Actually Decides What to Surface – We look at the core ranking signals (content relevance, authority, structure, freshness, brand reputation)
• The 5 Mistakes That Are Killing Your AI Visibility – We check common failure points that can be eliminated with generative engine optimization
• How to Audit Your Brand for AI Search Readiness – Here, we explore a practical, step-by-step self-audit framework.
• A Phased Plan to Rebuild Your AI Search Visibility – You also see a solid action roadmap for generative engine optimization from scratch.
• How to Track Whether It’s Working
• Why Textuar is Ideal for Your Generative Engine Optimization Content Needs
You have invested months – maybe years – into building your online presence. Your pages rank well on Google. You have earned backlinks from credible sources. Your content gets traffic and engagement. By every traditional metric, your brand is doing the right things.
So why is your brand disappearing from AI search?
Well, it may have something to do with Generative Engine Optimization.
This is the uncomfortable truth that marketers are only now beginning to confront. AI-powered search tools – Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini – are not just another layer on top of traditional search. They are fundamentally rewriting the rules of online visibility. And most brands are not ready for it.
The numbers make this impossible to ignore Generative Engine Optimization.
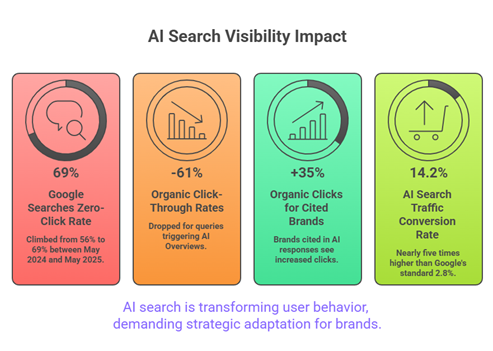
-Nearly 60% of Google searches now end without a single click to any website, with zero-click rates climbing from 56% to 69% between May 2024 and May 2025.
-Organic click-through rates for queries that trigger AI Overviews have dropped by 61%, while brands that are actually cited inside those AI responses see a 35% increase in organic clicks.
-Meanwhile, AI search traffic – while still small – converts at 14.2%, nearly five times higher than Google’s standard 2.8%.
The traffic is shrinking. The value of that traffic is rising. And the brands that figure out how to show up in AI-generated answers will be the ones that capture it. This is where Generative Engine Optimization comes to the fore.
This blog breaks down exactly why brands are losing visibility in AI search, what mistakes are accelerating that loss and – most importantly – how to diagnose and fix the problem from the ground up.
Why Your Brand is not on AI Search (Even if You Rank High on Google)?
Traditional SEO and AI search operate on fundamentally different logic – and most brands are still playing by the old rules.
When you rank on Google, you are competing for a position in a list of links. Users see your title, maybe a snippet of text and decide whether to click. The entire system is designed around getting people to your page.
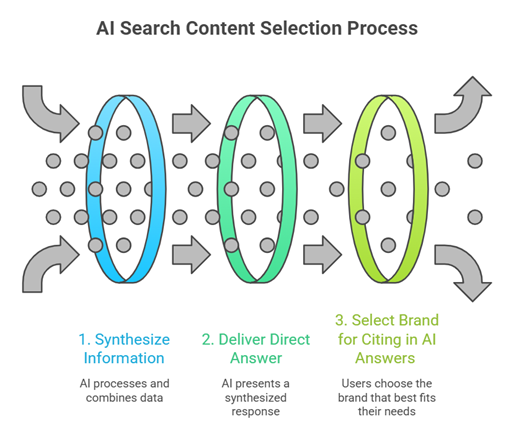
AI search skips that step entirely. Instead of presenting links for users to choose from, tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity and Google AI Overviews read across hundreds of sources, synthesize the information and deliver a direct answer. Your page does not need to be clicked for it to be used – but it does need to be chosen. And that is where most brands fall apart if a generative engine optimization plan is not in place.
Here is the core disconnect- A page can rank in the top three on Google and still be completely absent from every AI-generated answer on the same topic.
Ranking proves that Google’s algorithm considers your page relevant. It does not prove that your content is specific enough, trustworthy enough, or well-structured enough for an AI system to actually pull from when constructing an answer.
Let us take a simple example. A software company has a blog post titled “The Best Project Management Tools in 2025.” It ranks on page one for that keyword. But when someone asks ChatGPT, “What is the best project management tool for remote teams with more than 50 people?” – that blog post is useless in the absence of generative engine optimization. It does not address the specific use case. It does not speak to the intent behind the question. AI search does not reward broad coverage. It rewards precision.
This is why brands that have invested heavily in top-of-funnel, broad-keyword content are the ones feeling the sharpest decline. The content was built to attract clicks, not to answer specific questions. And in an era where 93% of searches in Google’s AI Mode end without a click, attracting clicks is no longer the only game in town (or even the most important one).
The gap between “ranking well” and “being visible in AI search” is real, it is widening and it requires a completely different approach to content strategy.
How AI Search Actually Decides What to Show (aka AI Citations)
AI search is not a mystery box. It follows a logic – and once you understand that logic, you can enable the same in your generative engine optimization plan. This way, the path to visibility becomes much clearer.
The process starts before any AI answer is generated. AI-powered search tools do not crawl the entire web in real time for every query. Instead, they pull from pre-filtered source pools – largely built from the same search indexes that power traditional engines.
Around 40% of AI citations come from Google’s top 10 results, which means traditional SEO still matters as an entry point. But getting into that pool is only the first gate.
What happens next is where most brands lose.
Once a source is eligible, AI systems evaluate it against five core signals to decide whether it actually gets cited in the answer-
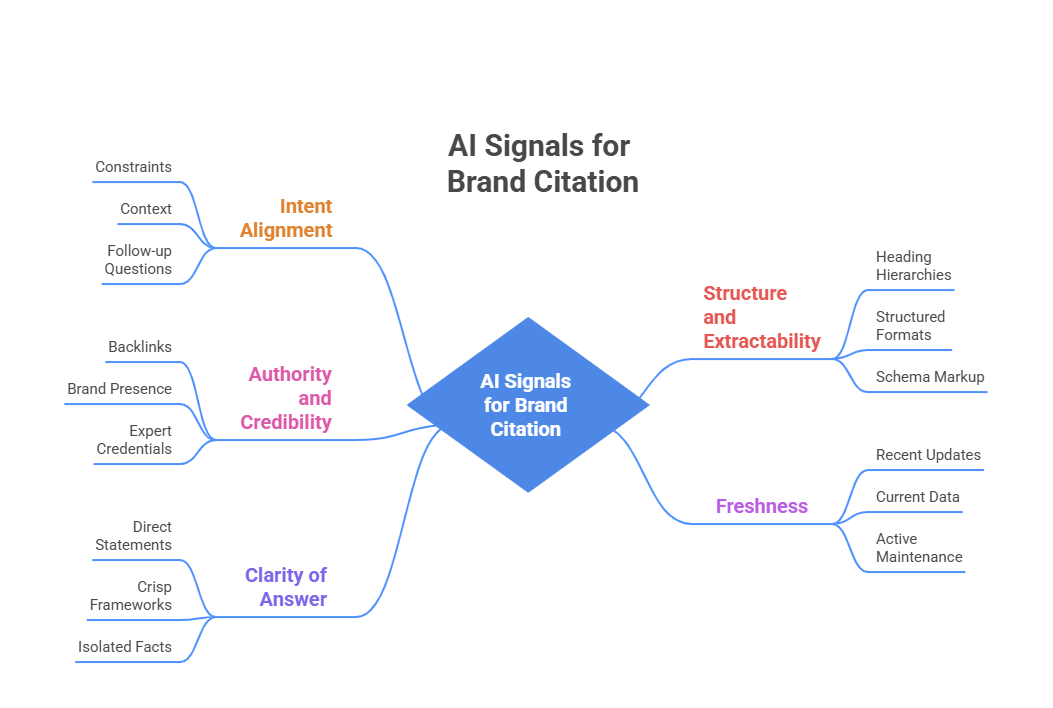
1. Intent alignment
AI search is built to answer specific questions, not surface broad topics. Content that directly addresses the exact intent behind a query – including the constraints, context and follow-up questions a user might have – is far more likely to be selected.
A detailed guide tailored to a narrow use case will beat a comprehensive overview every time, because it functions as a better answer to the specific question being asked.
2. Structure and extractability
AI systems do not read pages the way humans do. They parse content into segments and evaluate how clearly each piece of information is presented. Pages with clear heading hierarchies, well-organized sections and structured formats like tables or FAQs are significantly easier for AI to extract value from.
Research suggests that pages with clear H2 and H3 structures are roughly 40% more likely to be cited by Ai search engines. Similarly, proper FAQ and Article schema markup can increase citation likelihood by around 28%. And this forms the core of a robust generative engine optimization strategy.
3. Authority and credibility
AI tools want to reference sources that look trustworthy – not just on their own site, but as validated by the broader web. This includes backlinks and mentions from credible third-party sources, consistent brand presence across multiple platforms and clear authorship or expert credentials. If your SEO company rolls out a generative engine optimization campaign, this will perhaps be the most time-consuming activity in the plan.
Brands that appear on four or more trusted external platforms are roughly 2.8 times more likely to show up in ChatGPT responses. The signal AI is looking for is external confirmation, not self-declared expertise.
4. Content Freshness and Relevance
AI-powered search prefers content it can trust to be current. This is why a strong generative engine optimization plan should factor in content freshness. Pages that have been visibly updated recently, that reference current data and that show signs of active maintenance are treated as more reliable.
Content updated within the last 30 days earns roughly three times more citations than older material. This does not mean you need to rewrite everything constantly – it means stale, outdated pages are quietly being deprioritized.
5. Clarity of answer
AI systems favor content that leads with a direct answer rather than burying the point deep in the page. Short, definitive statements, crisp frameworks and isolated facts are the types of content that get pulled into AI-generated responses most often. If your page makes the reader work to find the answer, AI search will likely move on to a source that does not.
These five signals work together, not in isolation. A page that nails intent alignment but has no structure and no external validation will still be passed over. A page with perfect structure but outdated information loses credibility.
The brands that consistently show up in AI search are the ones whose content satisfies multiple signals at once – and does so repeatedly across related queries.
What are the Mistakes That Affect AI Visibility
Brands disappear from AI answers because of common errors that are easy to avoid – even with good traditional SEO. Between 40-60% of the visibility of AI decays on a monthly basis, often because of one of these mistakes-
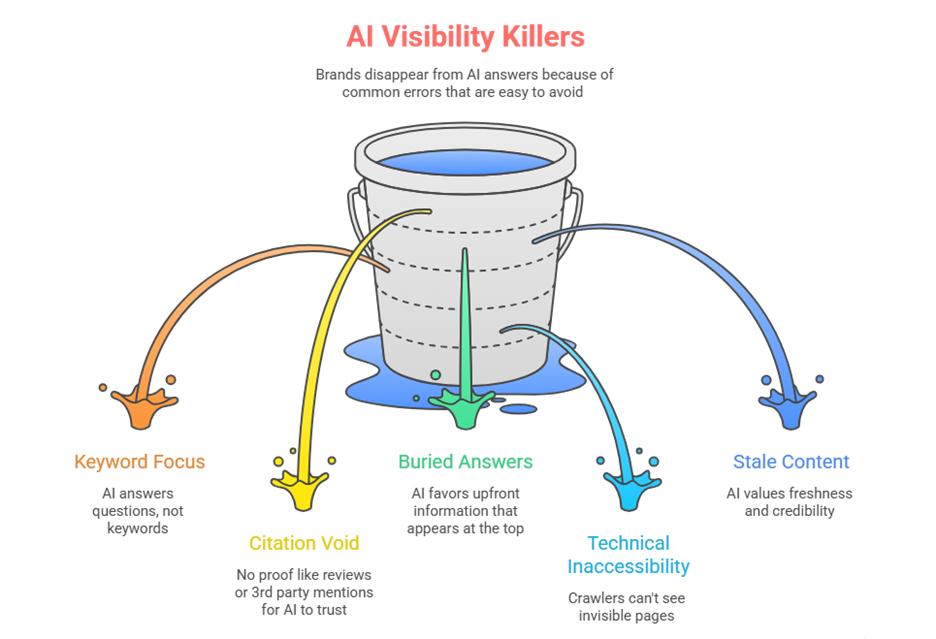
1. Writing for keywords, not questions
AI search doesn’t think in keywords such as “best CRM tools” – it answers specific questions and use cases. If your generative engine optimization content is constructed around broad keyword clusters, then your content will not be surfaced by AI for real user queries.
2. Existing in a citation void
With no third-party mentions, reviews or media coverage to provide proof, AI has little evidence to trust you. Up to 90% of citations on answers in AI are not from owned content. They are earned sources. Self-praise isn’t enough.
3. Burying the answer
AI extracts clear answers fast. If key information is hidden in paragraph six, AI will favor competitors who put the information upfront. Your generative engine optimization campaign should structure content for extractability, not just for readability.
4. Ignoring technical accessibility
AI crawlers can’t cite what they can’t see. Pages that rely on heavy JavaScript, block bots or have poor schema markup may be invisible, silently killing visibility.
5. Letting content go stale
AI values freshness. Outdated stats and out of date examples or product references lead to a loss of credibility and citations. Content updated within 30 days gets approximately 3X as many citations as old content.
Avoiding these mistakes in generative engine optimization makes sure that your brand is still giving visibility in the AI-powered search landscape.
Each of these mistakes compounds the others. A brand that writes for keywords, has no external citations, buries its answers, is technically inaccessible to AI crawlers and lets its content go stale is not just underperforming in AI search – it is functionally invisible. The good news is that every single one of these mistakes is diagnosable. And that is exactly what the next section covers.
How to do Generative Engine Optimization AI Readiness Audit?
| Audit Area | Key Question to Ask | Core Principle | Actionable Step |
| 1. Content & Intent | Does our content answer specific questions, not just target keywords? | AI matches user questions to direct answers. | Audit top pages- Rewrite broad topics into clear Q&A formats (e.g., “How to…” or “What is the best…for…”). |
| 2. External Validation (Citations) | Are credible third parties talking about us? | AI needs external proof to trust and cite you. | Build a PR/outreach plan to earn mentions in industry media, reviews and round-up articles. |
| 3. Content Structure | Can an AI easily find and extract the key answer on a page? | Prioritize extractability. Answers must be immediate. | Use clear headers, bullet points and place the direct answer in the first 100 words. |
| 4. Technical Accessibility | Can AI crawlers access and read our content? | Invisible to AI = not cited. | Audit robots.txt, ensure server-side rendering (or dynamic rendering) and implement schema markup. |
| 5. Content Freshness | Is our core content updated recently? | AI favors current, accurate data. | Establish a quarterly review cycle for high-value pages to update stats, examples and references. |
Before you optimize anything, you need to know where you actually stand. Most brands skip this step entirely – they assume that because their SEO is strong, their AI visibility must be too. That assumption is almost always wrong.
Fewer than one in ten AI-generated answers include a commercial brand, even when that brand dominates traditional search results in the same category. An audit closes that blind spot. Here is a step-by-step framework you can run internally before generative engine optimization, no specialized tools required.
Step 1- Run a visibility baseline across AI platforms
This is your starting point – and it takes less than an hour. Open ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google Gemini and Google’s AI Mode. Type in the exact questions your ideal customers would ask. Use specific, intent-driven queries, not broad keywords.
For example, do not search “project management software.” Instead, search “What is the best project management tool for a remote marketing team of 15 people?” For each query, note whether your brand appears at all, how it is described if it does, which competitors are mentioned instead and which sources are being cited.
Log everything in a simple spreadsheet. This baseline is your benchmark – everything else in the audit is measured against it.
Step 2- Map your top pages to real questions
Pull your five to ten highest-traffic pages. For each one, write down the specific question a user would have to ask for that page to be the ideal answer. Then ask yourself whether the page actually answers that question directly and early.
If the answer to either question is no, that page has an intent alignment gap. This is one of the fastest ways in generative engine optimization to identify why your content is being skipped. A page does not need to be rewritten from scratch – it just needs to be restructured so the relevant answer is front and center.
Step 3- Check your technical accessibility for AI crawlers
This is an important part of generative engine optimization readiness audit AI search tools cannot cite what they cannot read. This step is about making sure your pages are actually visible to automated systems. Verify that your robots.txt file is not blocking AI bots. Check whether your most important pages rely on client-side JavaScript rendering – if they do, AI crawlers may be seeing an empty page.
Run your top URLs through Google’s Rich Results Test to confirm your schema markup is valid and properly implemented. Look specifically for FAQ schema, Article schema and Organization schema. If any of these are missing or broken, that is a direct gap in your AI readiness.
Step 4- Evaluate your external validation footprint
AI search heavily weights how your brand appears outside your own website. For this step, search for your brand name across review platforms your customers actually use. Count how many credible third-party sources mention you – industry publications, comparison sites, review aggregators.
Check whether those mentions are consistent in tone and accuracy. If you find fewer than three to four credible external sources referencing your brand in a way that aligns with how you want to be perceived, you have a citation vacuum. That is one of the hardest gaps to close quickly, but it is also one of the most important to identify early.
Step 5- Assess content freshness across key pages
Go through your top pages and check when each was last genuinely updated – not just a cosmetic date change, but an actual revision of the content. This is a crucial part of your generative engine optimization readiness audit Flag any page where the statistics, examples, or product references are more than six months old.
Also look for references to tools, features, or data sources that no longer exist. Any page that has not been meaningfully reviewed in the last 30 days is already losing ground in AI citation frequency. Prioritize these pages for immediate review.
Step 6- Score and prioritize
Once you have completed the five steps above, you will have a clear picture of where your brand stands across the signals that matter most to AI search. Group your findings into three buckets-
– Quick wins that can be fixed within a week, such as schema corrections or page restructuring
– Medium-term fixes that require content updates or intent realignment; and
– Long-term gaps like external validation that require sustained effort over months. This prioritized view becomes the foundation for the phased optimization plan covered in the next section.
How to Build AI Search Visibility with Generative Engine Optimization
Knowing where you stand is only useful if you have a clear plan for where to go next. This section lays out a four-phase roadmap designed to build AI search visibility from the ground up – not by fixing everything at once, but by layering improvements in the order that matters most. Each phase builds on the one before it.
Skipping ahead without completing the earlier steps will not get you results in generative engine optimization. The reason is simple- AI search evaluates signals together, not in isolation.
| Phase | Core Goal | Key Actions | Output / Example |
| 1- Define & Map | Identify and map specific AI-driven questions to existing pages. | List 5–10 high-intent customer questions. Map each to a target page; identify gaps. | Example- “Best accounting tool for freelancers who invoice monthly?” → mapped to freelancer pricing page, revealing a missing invoicing workflow explanation. |
| 2- Align Content | Restructure pages to directly answer the mapped questions. | Answer the question clearly in the first few paragraphs. Use clear headings, FAQs and schema markup for AI parsing. | Example- Revise the freelancer page to lead with the monthly invoicing workflow and add FAQ schema. |
| 3- Build Trust | Increase credibility through on-page expertise and evidence. | Support claims with data, case studies and external links. Highlight original research and expert input. | Example- Add a case study showing faster payments and link to a third‑party review about invoicing speed. |
| 4- Earn Validation | Secure lasting visibility through external mentions and citations. | Pitch stories to publications, encourage reviews and monitor user‑generated forums. Focus on sources AI already trusts. | Example- Earn coverage in freelancer media and build reviews on G2/Capterra. Over time, AI citations rise due to third‑party signals |
Phase 1- Define what you want to be visible for
This is the most important phase and it requires no content changes at all. Before you optimize a single page, you need to decide which specific queries matter to your business. AI search does not reward broad presence – it rewards precision.
A brand that shows up in three highly relevant AI answers is in a far stronger position than one that half-appears in twenty.
Start by listing the five to ten questions your ideal customers are most likely to ask an AI tool at the moment they are closest to a purchase decision. These are not broad keywords. They are specific, intent-driven questions – the kind that include constraints, use cases, or comparison language.
Then map each question to a single page on your site that you want AI to reference when that question comes up. If no such page exists, that is your first content gap to address in generative engine optimization.
Example- A B2B accounting software company identifies “What is the best accounting tool for freelancers who invoice monthly?” as a high-priority query.
They map it to their freelancer pricing page – but realize that page currently lists features without ever addressing the invoicing workflow directly. That gap becomes the input for Phase 2.
Phase 2- Match your content to the questions you found
Now that you know which queries are important and which pages need to support the queries, you move to the second phase of the generative engine optimization plan. Here, the focus is on getting these pages to be able to answer the queries that they are supposed to, in the first place. AI search is a content-level evaluation of the query. A page which only makes a loose connection to a question will not be chosen, even if it ranks well in traditional search.
For each page that you mapped out in Phase 1, ask three questions-
-Will the page answer the basic question in the first few paragraphs?
-Does it represent the specific limitations or application scenario for the query?
-Does it anticipate the follow up questions a user would naturally ask next?
If the answer to any of these is no, then the page needs to be restructured – not necessarily rewritten from scratch, but rather reorganized so the most relevant information gets front and center, and supporting context comes in a logical sequence.
Add clear headings, a brief summary at the top and well-organized formats such as tables or FAQs where appropriate. Implement FAQ and Article schema markup to make the content easier for AI system to parse.
Example- The accounting software company re-writes the freelancer pricing page so the introduction section incorporates information about how the invoicing workflow works for monthly billing cycles.
They include a FAQ section to answer common issues raised by freelancers – tax reporting, late payment reminders and multi-currency support – with satisfaction of FAQ schema. The page takes the form of a direct answer to the original query, rather than simply a pricing table.
Phase 3- Make your content easier to trust
Once your pages have been aligned to the right questions and are structured in a manner that allows them to be easily extracted, the next issue in generative engine optimization is credibility. AI search does not just look at what your content says – it looks at whether there is reason to believe it. This is where on page authority signals come in.
Support claims with data, link to credible external sources where applicable and ensure your pages demonstrate real subject-matter knowledge – and not surface-level coverage of a topic. If you have original information, case studies, or expert insight on your content, highlight it.
These are the types of signals that give AI systems more confidence when deciding whether to cite a source: Pages that exhibit depth and specificity in a manner they have earned, rather than it being generic, will consistently be more referenced.
Example- The accounting software company has added a case study to the freelancer page showing how users who set up a monthly invoicing with its platform get paid an average of 12 days quicker.
Here they link to a third-party review of an accounting publication, which mentions the speed of the tool’s invoicing. These additions give the page a layer of credibility that goes beyond the company’s own claims – and that’s exactly what AI search is looking for.
Phase 4- Build external validation over time
This is the slowest phase – but it is also the one that creates the most durable visibility. AI search heavily weights how a brand appears outside its own website. Reviews, third-party mentions and coverage from credible industry sources all contribute to the external signal that tells AI systems a brand is legitimate and worth referencing.
This phase in AI search visibility boost using generative engine optimization is not a one-time push. It is an ongoing process of earning mentions from sources that AI already trusts. That means actively pursuing reviews on platforms your customers actually use, pitching content or data to industry publications and getting included in third-party comparisons or recommendation roundups.
User-generated content is also increasingly influential – Reddit citations in AI Overviews surged roughly 450% in a three-month window and user-generated content now makes up over 21% of all AI citations. Being present in conversations where AI already pulls information is one of the highest-leverage moves a brand can make.
Example- The accounting software company reaches out to three freelancer-focused publications and offers an exclusive stat from their own data – that freelancers using automated monthly invoicing reduce payment delays by nearly two weeks.
Two publications pick up the story. The company also encourages satisfied freelancer customers to leave detailed reviews on G2 and Capterra.
Over the following months, these external signals accumulate. When someone asks ChatGPT about accounting tools for freelancers, the brand starts appearing in the answer – not because of anything on their own site, but because the broader web is now confirming what their content claims.
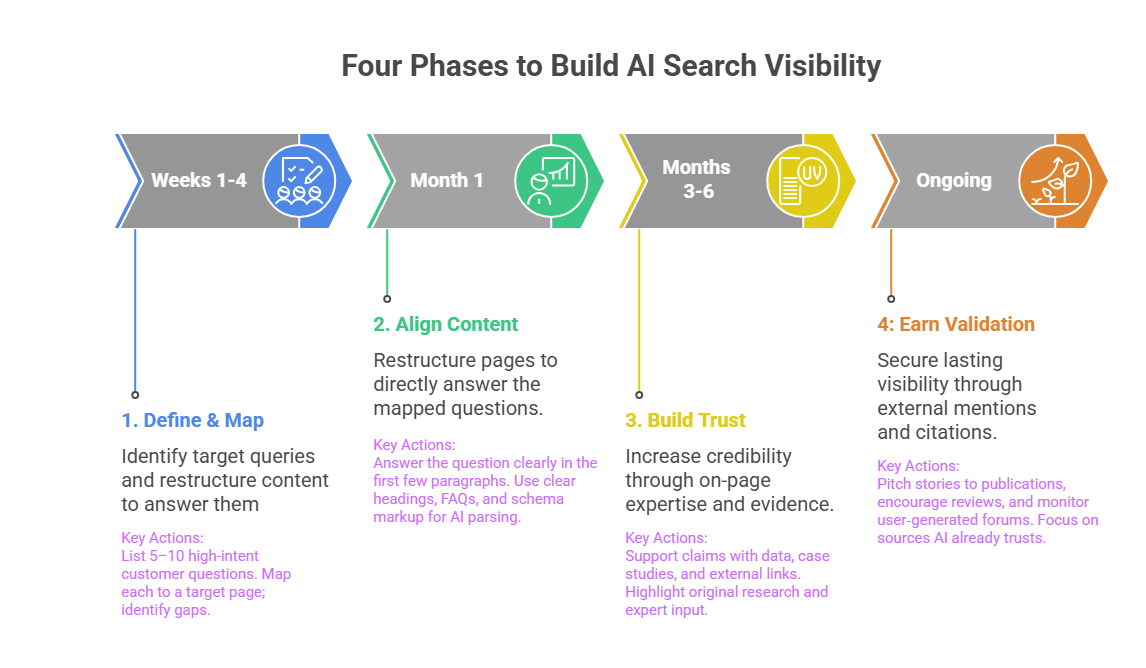
These four phases do not have a fixed timeline in the generative engine optimization process. Phase 1 and 2 can often be completed within two to four weeks. Phase 3 is ongoing but takes shape within the first month. Lastly, Phase 4 is a sustained effort that compounds over three to six months. The key is sequencing – each phase creates the conditions that make the next one possible.
How to Track if Generative Engine Optimization Plan is Working
Generative engine optimization without measurement is guesswork. There is no single dashboard that tells you everything about your AI search visibility yet – but there are four reliable methods that together give you a clear, ongoing picture of where you stand.
- Manual AI spot-checks
Run your priority queries directly in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini and Google AI Mode. Note whether your brand appears, how it is described and which competitors show up instead. Log results in a spreadsheet and repeat weekly. This is your fastest and most accessible baseline.
- Google Search Console AI filters
Go to Performance, then Search Results and add a filter for Search Appearance. If the AI Overview option is available, select it. You will see which of your URLs are being pulled into AI-generated snippets, along with impressions, clicks and the queries that triggered them.
- Google Analytics 4 custom channels
Create a custom channel group labeled “Generative AI” using source filters like chat.openai.com and perplexity.ai. This lets you isolate referral traffic coming specifically from AI tools and track how that traffic converts compared to other channels over time.
- Dedicated AI visibility tools
Platforms like OtterlyAI, LLMrefs and Frase AI Visibility automate prompt tracking across multiple AI engines simultaneously. They surface brand mentions, citation frequency, competitor benchmarking and sentiment shifts – saving you the manual effort and giving you trend data that a spreadsheet cannot.
Why Choose Textuar for Generative Engine Optimization
Building visibility in AI search requires more than generic content – it demands content that is strategically aligned to how answer engines discover, evaluate and cite sources. Textuar brings over 15 years of SEO and content expertise, now applied specifically to the demands of generative engine optimization.
1. GEO-ready content from day one
Textuar’s writers create blogs and articles specifically optimized for answer engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity – not just traditional search. Every piece is structured for AI extractability, with clear intent alignment and schema-ready formatting built into the workflow.
2. End-to-end project management
From initial research and requirement analysis to drafting, editing and final delivery, Textuar handles the entire content pipeline. This includes formatting content specifically for generative engines and AI LLMs, so you do not have to manage that layer yourself.
3. Deep industry specialization for generative engine optimization
With specialized writers across 23+ content verticals – technology, SaaS, healthcare, finance and more – Textuar produces content that demonstrates genuine subject-matter expertise. That depth is exactly what AI search like ChatGPT looks for when deciding which sources are credible enough to cite.
4. Scalable output without compromising quality
Textuar can deliver up to 18,000–20,000 words per day while maintaining SEO and AEO standards. Whether you need a single landing page rewrite or a full content audit across your site, the capacity is there – and so is the quality control.
FAQs – Generative Engine Optimization
1. Do traditional SEO practices still matter if I want to show up in AI search?
Yes, but they are no longer enough. Traditional SEO helps your content get discovered and indexed – what is still the first step to AI visibility. However, once your content is in the pool, AI search simply applies its own evaluation criteria around intent alignment, structure, freshness and external trust signals. This is why you need generative engine optimization to go beyond standard ranking factors.
2. Can I optimize my content specifically for ChatGPT or Perplexity?
No, not directly. These platforms do not publish ranking algorithms or take submissions. What you can do is optimize your content to meet the signals these systems already consider in your generative engine optimization plan. Here, you can ensure clear answers to specific questions, good structure, credible external validation and up-to-date information. Content that scores well on these signals tends to perform across all AI platforms, not just one.
3. Why do AI search results vary so much from platform to platform?
Each AI tool uses a different combination of data sources, retrieval methods and ranking logic. Google AI Overviews draws heavily from its own search index; Perplexity crawls the web in real time, and ChatGPT uses a combination of pre-trained knowledge and live retrieval. A brand can be present in one and not present in another. This is why achieving AI search visibility via generative engine optimization on multiple platforms is so important, and not optional.
4. How long will it take for generative engine optimization for AI Search?
It varies by phase. On-page changes such as restructuring the content and adding schema can generate early signals within two to four weeks. Building external validation through earned media and reviews is a slower process – typically three to six months before showing results. Consistency is more important here than speed. Brands that continue to work on generative engine optimization steadily realize exponential gains over time.
5. Will AI search hurt my brand if it misrepresents me?
Yes, and it is a real concern. AI tools can sometimes present information in an inaccurate way or in a context that doesn’t make sense. This is one of the reasons why it’s such an important to take control of your narrative with clear, well structured owned content in generative engine optimization. This gives AI systems the accurate source material to work from. Thus, monitoring how your brand is described in AI responses, not merely if it is present at all, is a critical part of any AI visibility strategy using generative engine optimization.
6. Do I need to create new content or can I get better at using what’s already there?
In most cases, you can start work on generative engine optimization by optimizing existing content. An audit framework is designed in this blog to identify those pages which are too close to being AI-ready but need a little restructuring work, freshening up or realignment of intent. New content is only necessary where there is no existing page that addresses a high-priority query adequately – which will be clearly surfaced by the audit.
7. How visible the search result is by AI is in fact down to how much of it I have control over.
More so than most brands realize. Intent alignment, content structure, schema markup, freshness and on page credibility signals are all within your direct control. External validation – reviews, media mentions, third-party citations – takes more effort but is something you can also take an active role in. The one area that no one has a huge amount of control over, is how each AI platform gives weight to these signals in its specifications, which is why optimizing broadly across them all is your safest and most effective bet.
The Bottom Line
AI search is not coming. It is already here; and it is already deciding which brands get seen and which ones get skipped. This is why you need generative engine optimization. After all, the rules are different from traditional SEO, but they are not unknowable.
They follow a logic built around specificity, structure, trust and external validation. Brands that understand that logic and act on it will not just survive this shift – they will own it.
The path forward is clear-
-know which queries matter to your business,
-align your content to answer them directly,
-make that content trustworthy and easy for AI to extract and
-build external credibility over time.
It is not complicated. But it does require intention, consistency and a willingness to stop optimizing for the old game and start playing the new one with generative engine optimization.
Connect with Textuar to know how you can emerge as a brand that figure out GEO first. This way, will not just show up in AI search. You will become the answers AI cannot ignore.